INTRODUCTION
Two positive developments in HIV management in recent years have been improved medicines and increased person-centeredness of care1-5. The latter emphasizes that in the treatment journey of people living with HIV (PLHIV), the ‘destination’ is not merely achieving viral control, but also attaining and maintaining good health-related quality of life. Indeed, improving health-related quality of life among ≥90% of PLHIV was proposed as the fourth ‘90’ target, in addition to the original clinically oriented targets of increasing the percentages of PLHIV diagnosed, on antiretroviral therapy (ART), and virally suppressed5-7. Viewed through the converging lenses of quality-of-life improvement and person-centered care8, patients must be engaged as partners in their own care. For patients to be empowered, they need to be both informed and involved9,10, concepts that are related yet distinct. Involvement in care can only be meaningful if patients are first well-informed, but being informed does not guarantee being involved in decision making. In contrast to meaningful involvement in decision making, information sharing may be a one-way flow, or may even be passive (e.g. patient education materials left at a doctor’s reception desk). Actively involving patients in decision making, on the other hand, is a dynamic process, founded on high-quality, two-way communication to elicit and incorporate patients’ values and preferences in the treatment plan9.
The need for tailored care is vital because PLHIV’s medical, social and economic circumstances vary, and different patients may respond to the same treatment differently. Enshrined in the practice of person-centered care for PLHIV are the core values of respect for persons and health equity11,12. The latter is particularly important because studies have consistently demonstrated poorer quality of life among PLHIV compared to the general population, including more comorbidities and high prevalence of polypharmacy13-15.
In 2019, there were an estimated 29045 PLHIV in Australia with higher prevalence reported among gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, people who inject drugs, people in custodial settings, as well as trans and gender-diverse people16. Australia has made major strides towards HIV/AIDS prevention and control; it was one of only 14 countries that met the UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets of diagnosis, ART coverage, and viral suppression during 201917. Yet, little is known regarding progress on the fourth ‘90’ target of improving quality of life among PLHIV – data that are important to inform clinical practice, programs, and policies. To fill this gap in knowledge, the objective of this study was to examine perceived treatment needs, challenges, and aspirations among PLHIV in Australia and contrast them with those in other countries. Specific questions explored were: 1) ‘What factors, including ART-related experiences, differ between PLHIV in Australia who perceive gaps in their overall HIV management versus those not perceiving gaps?’; 2) ‘What ART-specific challenges are reported among PLHIV in Australia, and how do perceived unmet needs influence reported treatment preferences?’; and 3) ‘To what extent are PLHIV in Australia informed and involved when making ART choices, and what is the association between the extent of engagement and indicators of health-related quality of life?’.
METHODS
Study population/sampling approach
We analyzed data from the web-based, cross-sectional survey called ‘Positive Perspectives’ which was conducted among adult PLHIV aged ≥18 years on ART in 25 countries during 2019 (pooled N=2389, Figure 1). Sampling was non-probabilistic and was done using targeted, convenience, and snowball sampling in each of the 25 countries. Within the cross-country survey, sample size ranged from 50 to 400. Administration of the surveys was done in the major language(s) spoken in each country. Of 120 participants from Australia, 56 were sampled from existing panels of confirmed HIV sero-positive individuals, while 64 were recruited from national, regional, and local charities/support groups for PLHIV. Ethical review was provided by the Pearl Institutional Review Board (No. 18–080622). The survey details have been published elsewhere.9,10,15,18,19
Measures
Self-reported health status and behaviors
Self-rated health as good/very good was classified as optimal (vs very poor/poor/neither good nor poor). Self-reported virologic control was defined as a response of undetectable or suppressed to the question: ‘What is your most recent viral load?’. Polypharmacy was defined as taking ≥5 pills per day for HIV or non-HIV conditions, or currently taking medicines for ≥5 conditions, including HIV15. Suboptimal adherence was defined as a report of ≥1 reason for missing ART ≥5 times within the past month19. Individuals diagnosed ≥1 year ago were classified as being treatment experienced.
Treatment challenges and unmet needs
Participants were classified as being satisfied with their ART if they answered ‘satisfied/very satisfied’ (vs ‘very dissatisfied’, ‘dissatisfied’, ‘neither satisfied nor dissatisfied’) to the question: ‘Overall, how satisfied are you with your current HIV medication?’. A report of ART side effects was an answer of ‘agree/strongly agree’ (vs ‘disagree/strongly disagree/neither agree nor disagree’) to the statement: ‘My current HIV medication gives me side effects’. Data were also collected on the type of side effects experienced (presence or absence of gastrointestinal symptoms), and severity (perception that it ‘impacted’ their lives, and whether they missed ART because of side effects in the past month). Furthermore, concerns regarding long-term side effects and other adverse treatment effects were assessed, including worries about having to take more and more medicines, the potential for drug–drug interactions, potential adverse impact of ART on their body and/or body shape, as well as the impact on their overall health and wellbeing.
Data were also collected on confidentiality concerns with ART, perceived comfort sharing their HIV status, with whom they had shared their status, reasons for refusing to share in the past, and secretive behaviors such as hiding/disguising HIV medications or skipping ART doses in the past month because of privacy concerns. Participants also indicated whether at the time of the survey, they perceived room for improvement with their HIV management overall (i.e. ‘I feel there is room for improving the way my HIV is managed’), as well as with their ART (i.e. ‘I feel that there is room for improvement with my current HIV medication’).
Treatment preferences and aspirations
PLHIV’s favorability towards specific ART attributes was captured in many ways using absolute, relative, and time-varying assessments: A) with the absolute approach, two ART attributes (‘fewer medicines’, and non-daily dosing) were assessed in stand-alone questions to ascertain participants’ favorability on each feature separately without considering any other attribute; B) with the relative approach, seven ART attributes (including the two above, Figure 2) were assessed together, and participants ranked their choice (1st to 7th) of perceived importance for each attribute relative to all the other attributes; and C) with the time-varying approach, participants were presented with two period scenarios – now and when they first started ART. For each period, they selected what they consider(ed) most important from a list of multiple treatment goals (including many aspects of the attributes identified in A and B above, Table 1). Regarding analytical sample sizes, A was assessed among all 120 participants, B was open to all participants but completed by 110 respondents, C was assessed among 117 participants diagnosed with HIV for ≥1 year and who conceivably were on treatment long enough to make a meaningful ‘then vs now’ comparison.
Figure 2
Adjusted prevalence ratios for ever switching ART by country, compared to participants in Australia among an international sample of people living with HIV (N=2389)
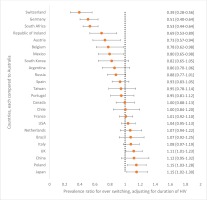
Table 1
Comparisons of treatment-related challenges and unmet needs between PLHIV in Australia, overall and stratified by whether or not they perceived gaps in their HIV management
Self-reported extent of being informed and involved in care
Perceived comfort raising various health concerns with HCPs and reported frequency of receiving health information on a variety of health topics from HCPs, were assessed. Participants were classified into three categories based on the extent to which they were both informed of new treatment options by their HCP and involved when making new treatment decisions: 1) Neither informed or involved, 2) informed but not involved, and 3) fully involved. Operationally, we used these two constructs to measure ‘informed’ and ‘involved’ status, respectively: ‘My provider tells me about new HIV treatment options that become available’ and ‘My provider seeks my views about treatment before prescribing an HIV medication’. Answers of ‘agree/strongly agree’ were classified as affirmative responses. The survey further asked participants whether they had ever wanted a different ART from the one they were taking and had communicated that preference to their HCP.
Analyses
Data were summarized using means and percentages. Among participants who completed the choice-based conjoint rankings of improvements to HIV medicines (n=110), we estimated the percentage of those who ranked each of the seven attributes in first place. Crude comparisons of prevalence were done with chi-squared tests, and age- and sex-adjusted comparisons were done using a Poisson regression model. To explore provider willingness to prescribe, and PLHIV willingness to switch to new medication, we compared the likelihood of ever changing ART across countries, adjusting for duration of HIV, as this might influence switching frequency. Where appropriate, free-text responses from participants were also explored to provide additional context to the quantitative data. All statistical tests were two-tailed and performed at p<0.05 using Stata Version 14.0. Unless otherwise specified, all results presented are for Australian participants.
RESULTS
Australian participants reported a mean (SD) age of 49.8 (11.4) years, and mean duration of HIV of 16.3 (10.8) years. Overall, 54.2% (65/120) were aged ≥50 years, 88.3% (106/120) identified as male; and 66.7% (80/120) were diagnosed with HIV pre-2010. Furthermore, 73.3% (88/120) lived in a metropolitan area, and 96.7% (116/120) reported viral suppression. Self-rated optimal health was as follows: physical 69.2% (83/120), mental 65.0% (78/120), sexual 54.2% (65/120), and overall 64.2% (77/120).
Treatment experiences, challenges and unmet needs
Overall, 48.3% (58/120) had concerns about taking more medicines as they grew older, 37.5% (45/120) worried about DDIs, and 63.3% (76/120) worried about the long-term impact of HIV medicine (Figure 1). Furthermore, 30.8% (37/120) reported currently experiencing ART side effects; prevalence was higher among those newly diagnosed during 2017–2019 (60.0%; 6/10) versus 2010–2016 (20.0%; 6/30) (p=0.014) or pre-2010 (31.3%; 25/80) (p=0.034). This disparity by year of diagnosis was even more marked within cross-country comparisons. Within country-specific analyses involving all participants, Australia ranked among countries with the lowest reported overall prevalence of side effects – higher than only Italy (25.0%; 30/120), and Canada (30.0%; 36/120). However, within analyses restricted to newly diagnosed individuals only, Australia ranked as one of the highest prevalence countries – lower than only Poland (62.5%; 5/8), the US (66.4%; 89/134), China (75.0%; 12/16), and Mexico (94.4%; 17/18).
Of the Australian participants experiencing side effects with their current ART, 56.8% (21/37) reported gastrointestinal symptoms. Compared to those not reporting any ART side effects, current side effect experience was associated with significantly higher prevalence of being worried about: drug–drug interactions [56.8% (21/37) vs 28.9% (24/83), p=0.004], long-term side effects [86.5% (32/37) vs 53.0% (44/83), p=0.002], unknown future adverse events [75.7% (28/37) vs 56.6% (47/83), p=0.047], and their overall wellbeing [75.7% (28/37) vs 51.8% (43/83), p=0.014]. Of all Australian participants who reported being concerned about ‘the long-term impact of HIV treatment’ within the past year, the percentage who reported that they had ‘changed [their] HIV medication’ within that past-year period to ‘reduce [this] concern’ was 29.0% (27/93), the highest in all participating countries. When examining changing of ART over a much longer window period – from the point of treatment initiation – 85.8% (103/120) of participants in Australia reported ever switching. After adjusting for duration of HIV, the probability of switching ART was 11% higher in the UK, 15% higher in Poland, and 15% higher in Japan, when compared to Australia. However, the probability was significantly lower, by 20% to 60%, in the following countries compared to Australia: Switzerland, Germany, South Africa, Ireland, Austria, Belgium, and Mexico (Figure 2). Other countries did not differ significantly from Australia in switching. Side effects were the commonest reason for switching ART in Australia (54.4%; 56/103). Other reasons were to reduce the number of pills (33.0%; 34/103), reduce the number of medicines (25.2%; 26/103), because of ART resistance (13.6%; 14/103), to reduce drug–drug interactions (6.8%; 7/103), and cost (5.8%; 6/103). Notably, 21.4% (22/103) changed ART because of some ‘other’ reason not belonging to any of the well-defined categories above, including because of ‘A more effective combination therapy’, ‘Better treatment’, ‘Better version of the last one I was taking’, ‘Blood brain barrier’, ‘Concerns over body fat redistribution’, ‘Osteoporosis’, ‘Possible side effect’, ‘Pregnancy’, ‘Previous medication was causing kidney [problem]’, ‘Recommended by doctor’, ‘Reduce possibility of heart incidents’, ‘Reformulated’, ‘Switch to a newer medication’, ‘The ability to take with food’, ‘To be on same medication as my partner’, and ‘Less impactful on the body’.
Of those who changed ART because of side effects, the top two co-existing triggers that were also reported were desire to reduce their pill intake (32.1%; 18/56), and desire to reduce their medicine intake (23.2%; 13/56). Within the context of cross-country comparisons, participants in Australia reported one of the highest percentages of those who ever switched ART ≥1 time in lifetime because of side effects and one of the lowest who skipped ART ≥5 times in the past month because of side effects (1.7%; 2/120).
By HIV duration, a higher percentage of those recently diagnosed during 2017–2019 reported concern about the impact of ART on their body/shape (90.0%; 9/10) versus 2010–2016 (50.0%; 15/30, p=0.005) but did not differ from pre-2010 (78.8%; 63/80, p=0.269). Adherence anxiety was highest among those diagnosed during 2017–2019 (80.0%; 8/10) versus 2010–2016 (36.7%; 11/30) (p=0.007) or pre-2010 (28.8%; 23/80) (p<0.001).
Overall, 81.7% (98/120) of participants in Australia reported a non-HIV comorbidity; 51.7% (62/120) reported polypharmacy (Table 1). Participants with polypharmacy reported a higher prevalence of being worried about taking more and more medicines as they grew older than those without polypharmacy [58.1% (36/62) vs 37.7% (22/58), p=0.027]. Older adults aged ≥50 years reported significantly higher prevalence of polypharmacy than those aged <50 years [63.1% (41/65) vs 38.2% (21/55), p=0.007] even though the percentage of those reporting ≥1 comorbidity did not differ significantly between the two groups [87.7% (57/65) vs 74.6% (41/55), respectively, p=0.064]. By specific conditions, however, those aged <50 years reported significantly higher prevalence of substance use disorder than those aged ≥50 years [21.8% (12/55) vs 7.7% (5/65), p=0.027], but significantly lower prevalence of arthritis [12.7% (7/55) vs 27.7% (18/65), p=0.044], cancer [7.3% (4/55) vs 20.0% (13/65), p=0.046], hypercholesterolemia [7.3% (4/55) vs 40.0% (26/65), p<0.001], and hypertension [10.9% (6/55) vs 33.8% (22/65), p=0.003]. All other assessed conditions did not differ significantly between the two age groups.
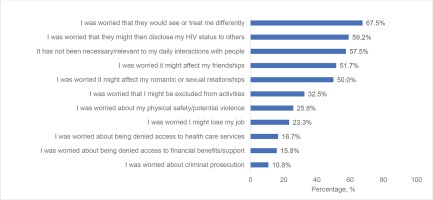
Psychosocial challenges were also reported: uncomfortable sharing their HIV status 56.7% (68/120); disguising/hiding their HIV medications 35.8% (43/120); would be stressed if someone saw their HIV medication 35.0% (42/120); missed ART ≥1 time in the past month because of privacy concerns 7.5% (9/120). The following estimates describe the percentages who reported not sharing their HIV status with the indicated person (among those reporting the assessed relationship): with a parent, child or sibling 18.8% (22/117); with other HCPs other than main HIV care provider or family doctor 16.5% (19/115); with their spouse/partner 7.9% (5/63); and with their family doctor 5.6% (6/108). ART-related secretive behaviors were most prevalent among those more recently diagnosed. For example, hiding/disguising HIV medication was 60.0% among both groups diagnosed during 2017–2019 (6/10) and 2010–2016 (18/30), versus pre-2010 (23.8%; 19/80, p<0.001). Similarly, the percentage who had shared their HIV status with a parent, child or sibling was 55.6% (5/9), 63.3% (19/30), and 91.0% (71/78), among those diagnosed during 2017–2019, 2010–2016, and pre-2010, respectively (p=0.001). Reasons for refusing to share HIV status in the past among all surveyed participants in Australia are shown in Figure 3.
Treatment preferences and aspirations
Overall, 83.3% (100/120) reported satisfaction with their current ART, yet, 84.0% (84/100) of these individuals were optimistic that future advances in HIV care would improve their health. When assessed as separate attributes, 85.0% (102/120) of sampled Australian participants were open to ART with fewer medicines, while 55.0% (66/120) were favorable towards non-daily (longer-acting) ART. Participants with polypharmacy were more open to ART with fewer medicines than those without polypharmacy [91.9% (57/62) vs 77.6% (45/58), p=0.028]. Individuals who had ever refused to share their HIV status for fear of romantic discrimination were more likely to favor a long-acting HIV regimen than those not reporting fear of romantic discrimination [65.0% (39/60) vs 45.0% (27/60), p=0.028], as well as those afraid of being denied health benefits [85.0% (17/20) vs 49.0% (49/100), p=0.003].
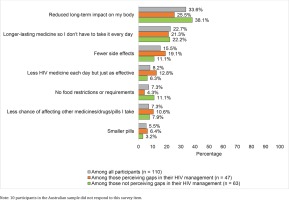
In ranked choice of ART attributes deemed most important (Figure 4), reducing long-term side effects had the highest percentage for first place (33.6%), followed by long-acting regimens (22.7%), fewer side effects (15.5%), fewer medicines (8.2%), reduced drug–drug interactions (7.3%) less food–drug interactions (7.3%), and smaller sized pills (5.5%). When comparing those with versus without perceived gaps in their HIV management, the former reported numerically higher rankings for attributes addressing more acute treatment effects (e.g. side effects, number of medicines, pill size, and drug–drug interactions); those not perceiving gaps in their HIV care reported numerically higher rankings for contextual or longer-term treatment effects (e.g. dosing conditions, and long-term side effects, Figure 4).
Figure 4
Percentage of participants in Australia who ranked each of the assessed improvements to HIV medicines in the first place of importance, overall and stratified by whether or not they perceived gaps in their HIV management
Evolution in treatment priorities were seen; Table 2 shows the percentage of treatment experienced persons who reported each treatment goal as something they prioritized then (time of starting treatment) as well as now (time of survey). Overall, the following treatment goals saw a 10–30 percentage points (PP) increase in perceived priority: preventing transmission to a partner (30 PP), minimizing the long-term impact of HIV treatment (23 PP), keeping the number of medicines in ART at a minimum (21 PP), preventing drug–drug interactions (18 PP), ensuring side effects are minimal (16 PP), and ensuring dosing flexibility (13 PP). Older adults reported a higher prevalence than those aged <50 years for reporting that minimizing the long-term impact of HIV treatment was one of their current treatment priorities [83.1% (54/65) vs 59.6% (31/52), p=0.005].
Table 2
Percentage of treatment-experienced* participants in Australia who selected each of the assessed treatment goals as something important to them when they first started treatment and now, overall and stratified by selected psychographic and demographic characteristics (N=117)
Self-reported extent of being informed and involved in care
Of the Australian participants experiencing side effects with their current ART, 81.1% (30/37) felt comfortable discussing side effects with their HCPs – the highest prevalence in all surveyed countries; this percentage was even higher when assessed among all participants overall as shown in Figure 5. Australian participants also reported the highest percentage (93.3%; 42/45) of those reporting that they discussed with their HCP about a treatment they wanted, among those indicating they ever wanted a new treatment. In addition, 75.8% (91/120) reported ‘My provider seeks my views about treatment before prescribing an HIV medication’, while 74.2% (89/120) acknowledged that their HCP told them of new treatments that are available (Figure 5). Although older Australian adults were more likely than their younger counterparts (i.e. <50 years) to report that their HCP often told them of new treatments that are available [84.6% (55/65) vs 61.8% (34/55), respectively, p=0.004], they did not differ significantly in the percentage who had ever told their HCP of a new treatment they wanted [38.5% (25/65) vs 30.9% (17/55), respectively, p=0.387].
Figure 5
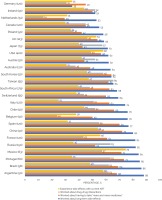
Selected indicators of understanding of their treatment and extent of their engagement with healthcare providers among people living with HIV in Australia and 24 other countries, 2019
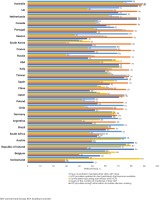
Markers of knowledge also demonstrated that sampled PLHIV in Australia understood their treatment well. For example, 85.0% (102/120) reported their HCP gave them ‘enough information’ to be involved in making choices, 88.3% (106/120) were aware of the number of medicines in their ART regimen, and 87.5% (105/120) were confident to report: ‘I understand enough about my HIV treatment’ – all three indicators in Australia were among the highest across all countries. High self-efficacy towards maintaining adherence was also reported: the percentage who reported having no problems with managing their daily oral ART was 80.8% (97/120), higher than everywhere else.
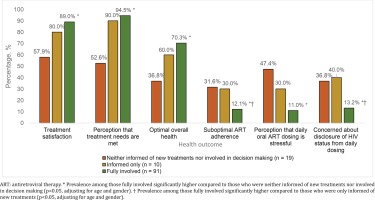
High involvement in care was associated with favorable health outcomes (Figure 6). For example, in age- and sex-adjusted comparisons within the Australian sample, those fully involved reported significantly higher prevalence of positive outcomes compared to those neither informed nor involved, including outcomes such as treatment satisfaction [89.0% (81/91) vs 57.9% (11/19), p=0.032], sentiment that their personal needs were met by their provider [94.5% (86/91) vs 52.6% (10/19), p=0.012], and optimal overall health [70.3% (64/91) vs 36.8% (7/19), p=0.032]; they were also less likely to report being stressed by their daily dosing schedule [11.0% (10/91) vs 47.4% (9/19), p=0.001]. Furthermore, those fully involved reported the lowest prevalence of suboptimal adherence, at 12.1% (11/91), dramatically lower than those only informed (30.0%; 3/10, p=0.040), or those neither informed nor involved (31.6%; 6/19, p=0.049). Similarly, the percentage of participants with ART confidentiality concerns was significantly lower among those fully involved (13.2%; 12/91) compared with those only informed (40.0%; 4/10, p=0.009), or neither informed nor involved (36.8%; 7/19, p=0.031).
Figure 6
Prevalence of health-related, self-reported outcomes among participants in Australia, stratified by extent of engagement with their healthcare providers in their treatment planning
Several barriers to discussing health issues with HCPs were reported by participants in Australia: 14.2% (17/120) were afraid of taking up the HCP’s time; 13.3% (16/120) did not want to be perceived as a ‘difficult patient’; 11.7% (14/120) felt little could be done to help them; and 10.8% (13/120) felt the issue was not important enough to be raised. Furthermore, 8.3% (10/120) said it was difficult for them to bring up the problem; 7.5% (9/120) reported each of the following barriers: doctor knows best, not confident, and not having the opportunity/time; while 5.0% (6/120) felt their HCP’s priorities were different from theirs. Younger adults aged <50 years reported higher prevalence than those aged ≥50 years for the following barriers: not confident enough [12.7% (7/55) vs 3.1% (2/65), p=0.046]; difficulty bringing up the issue [14.6% (8/55) vs 3.1% (2/65), p=0.024]; perception that the issue was not important enough to be raised [18.2% (10/55) vs 4.6% (3/65), p=0.017]; and fear of being perceived as a difficult patient [21.8% (12/55) vs 6.2% (4/65), p=0.012]. All other differences were statistically non-significant.
DISCUSSION
This study of Australian PLHIV currently taking antiretroviral treatment demonstrated that: 1) the presence of optimal HIV-related outcomes does not preclude unmet clinical needs, with 96.7% reporting viral suppression (similar to the 95% estimate from the 2018 national surveillance data)20, yet 35% overall reported suboptimal mental health and 42.5% felt there was room for improving their HIV management; 2) treatment satisfaction, though high (83.3%), was mingled with varying levels of concern over current and future adverse treatment effects, and twice more people worried about future side effects (63.3%) than currently experiencing them (30.8%). Treatment plans should therefore be regularly evaluated even when patients appear satisfied with their treatment and should be pre-emptive to address concerns about long-term impact of ART on kidneys, bones, and the liver – care that meets their needs and is based on the best scientific knowledge21.
Perceived priorities were related to underlying treatment challenges. For example, those with polypharmacy reported greater concerns about taking more and more medicines with age and were more open towards ART with fewer medicines than those without polypharmacy15. Medical advances in the treatment of HIV now include more potent, convenient, and well-tolerated regimens that allow people with HIV to maintain viral suppression while keeping HIV as a less conspicuous part of their lives1. Informing PLHIV about new treatments alone is, however, not sufficient; patients must be actively involved in treatment planning as our results show more favorable health outcomes among those actively engaged in their own treatment.
HCPs must be responsive to the broader psychological, social, and functional needs of PLHIV22-24. A holistic approach towards care is important given the unique needs of various key segments of our study population, including older adults25. Previous studies have shown that living with HIV can create unique challenges that can negatively affect physical and/or mental health26. Ageing may also bring additional health challenges for PLHIV, including multimorbidity and polypharmacy15. Fragmented care can further complicate challenges such as polypharmacy. A well-integrated and person-centered approach is therefore paramount.
To meet the range of needs of PLHIV across the continuum of their care, equitable access to healthcare and coordination of care is needed. This includes strengthening channels of patient-provider communication. While some individual-level communication barriers can be addressed by improving PLHIV’s self-efficacy, it is equally important to address broader barriers at the levels of health systems. In our study, older adults were less likely to cite personal challenges as barriers to communication (e.g. lack of confidence, fear of being labelled a ‘difficult patient’, difficulty bringing up the issue, or perceiving the issue as trivial); however, they did not differ from younger adults in their reported prevalence of more systemic barriers (e.g. perceived lack of time with HCPs during consultations). Enhanced and sustained efforts to dismantle barriers to quality communication may improve PLHIV’s quality of life. Although Australia performed favorably compared to other countries regarding various indicators of patient–provider engagement and PLHIV understanding of their treatment, these percentages while high, were all short of 90% – the minimum proposed target for measures of health-related quality of life within the framework of the fourth ‘90’5. There is, therefore, still room for improvement if we are to reach this fourth ‘90’ target.
Strengths and limitations
This study’s strength lies in its exploration of the ‘patient's voice’ using data from PLHIV from 25 countries covering almost every continent. Some limitations however exist to this study. First, these data are cross-sectional in nature, and only associations can be drawn. Second, the web-based survey and the convenience sampling may limit the study’s generalizability. Despite these limitations, this study provides important data for better understanding PLHIV’s needs and preferences in line with the fourth ‘90’ target.
CONCLUSIONS
Despite most participants reporting viral suppression (96.7%) and treatment satisfaction (83.3%), unmet needs existed and many PLHIV were worried about side effects and long-term impacts of ART. Side effects were the most common reason for switching ART and mitigating long-term side effects was deemed the most important improvement to HIV medicines. To meet the fourth ‘90’ target and improve health-related outcomes, it is important to educate PLHIV on new treatment options and actively engage them in shared decision making.